rnalysis.filtering.CountFilter.split_kmeans
- CountFilter.split_kmeans(n_clusters: PositiveInt | List[PositiveInt] | Literal['gap', 'silhouette', 'calinski_harabasz', 'davies_bouldin', 'bic'], n_init: PositiveInt = 3, max_iter: PositiveInt = 300, random_seed: NonNegativeInt | None = None, power_transform: bool = True, plot_style: Literal['all', 'std_area', 'std_bar'] = 'all', split_plots: bool = False, max_n_clusters_estimate: PositiveInt | Literal['auto'] = 'auto', parallel_backend: Literal['multiprocessing', 'loky', 'threading', 'sequential'] = 'loky', gui_mode: bool = False) Tuple[CountFilter, ...] | Tuple[Tuple[CountFilter, ...], ...]
Clusters the features in the CountFilter object using the K-means clustering algorithm, and then splits those features into multiple non-overlapping CountFilter objects, based on the clustering result.
- Parameters:
n_clusters (int, list of ints, 'gap', 'silhouette', 'calinski_harabasz', 'davies_bouldin', or 'bic') – The number of clusters the algorithm will seek.
random_seed (Union[int, None] or None (default=None)) – determines random number generation for centroid initialization. Use an int to make the randomness deterministic.
n_init (int (default=3)) – number of time the k-medoids algorithm will be run with different medoid seeds. The final results will be the best output of n_init consecutive runs in terms of inertia.
max_iter (int (default=300)) – maximum number of iterations of the k-medoids algorithm for a single run.
power_transform (bool (default=True)) – if True, RNAlysis will apply a power transform (Box-Cox) to the data prior to clustering.
plot_style ('all', 'std_area', or 'std_bar' (default='all')) – determines the visual style of the cluster expression plot.
split_plots (bool (default=False)) – if True, each discovered cluster will be plotted on its own. Otherwise, all clusters will be plotted in the same Figure.
max_n_clusters_estimate (int or 'auto' (default='auto')) – the maximum number of clusters to test if trying to automatically estimate the optimal number of clusters. If `max_n_clusters_estimate`=’default’, an appropriate value will be picked automatically.
parallel_backend (Literal[PARALLEL_BACKENDS] (default='loky')) – Determines the babckend used to run the analysis. if parallel_backend not ‘sequential’, will calculate the statistical tests using parallel processing. In most cases parallel processing will lead to shorter computation time, but does not affect the results of the analysis otherwise.
- Returns:
if n_clusters is an int, returns a tuple of n_clusters CountFilter objects, each corresponding to a discovered cluster. If n_clusters is a list, returns one tuple of CountFilter objects per value in n_clusters.
- Examples:
>>> from rnalysis import filtering >>> dev_stages = filtering.CountFilter('tests/test_files/elegans_developmental_stages.tsv') >>> dev_stages.filter_low_reads(100) Filtered 44072 features, leaving 2326 of the original 46398 features. Filtered inplace. >>> clusters = dev_stages.split_kmeans(14,power_transform=True) Filtered 44072 features, leaving 2326 of the original 46398 features. Filtered inplace. Filtered 1801 features, leaving 525 of the original 2326 features. Filtering result saved to new object. Filtered 2010 features, leaving 316 of the original 2326 features. Filtering result saved to new object. Filtered 2059 features, leaving 267 of the original 2326 features. Filtering result saved to new object. Filtered 2102 features, leaving 224 of the original 2326 features. Filtering result saved to new object. Filtered 2185 features, leaving 141 of the original 2326 features. Filtering result saved to new object. Filtered 2186 features, leaving 140 of the original 2326 features. Filtering result saved to new object. Filtered 2200 features, leaving 126 of the original 2326 features. Filtering result saved to new object. Filtered 2219 features, leaving 107 of the original 2326 features. Filtering result saved to new object. Filtered 2225 features, leaving 101 of the original 2326 features. Filtering result saved to new object. Filtered 2225 features, leaving 101 of the original 2326 features. Filtering result saved to new object. Filtered 2241 features, leaving 85 of the original 2326 features. Filtering result saved to new object. Filtered 2250 features, leaving 76 of the original 2326 features. Filtering result saved to new object. Filtered 2259 features, leaving 67 of the original 2326 features. Filtering result saved to new object. Filtered 2276 features, leaving 50 of the original 2326 features. Filtering result saved to new object.
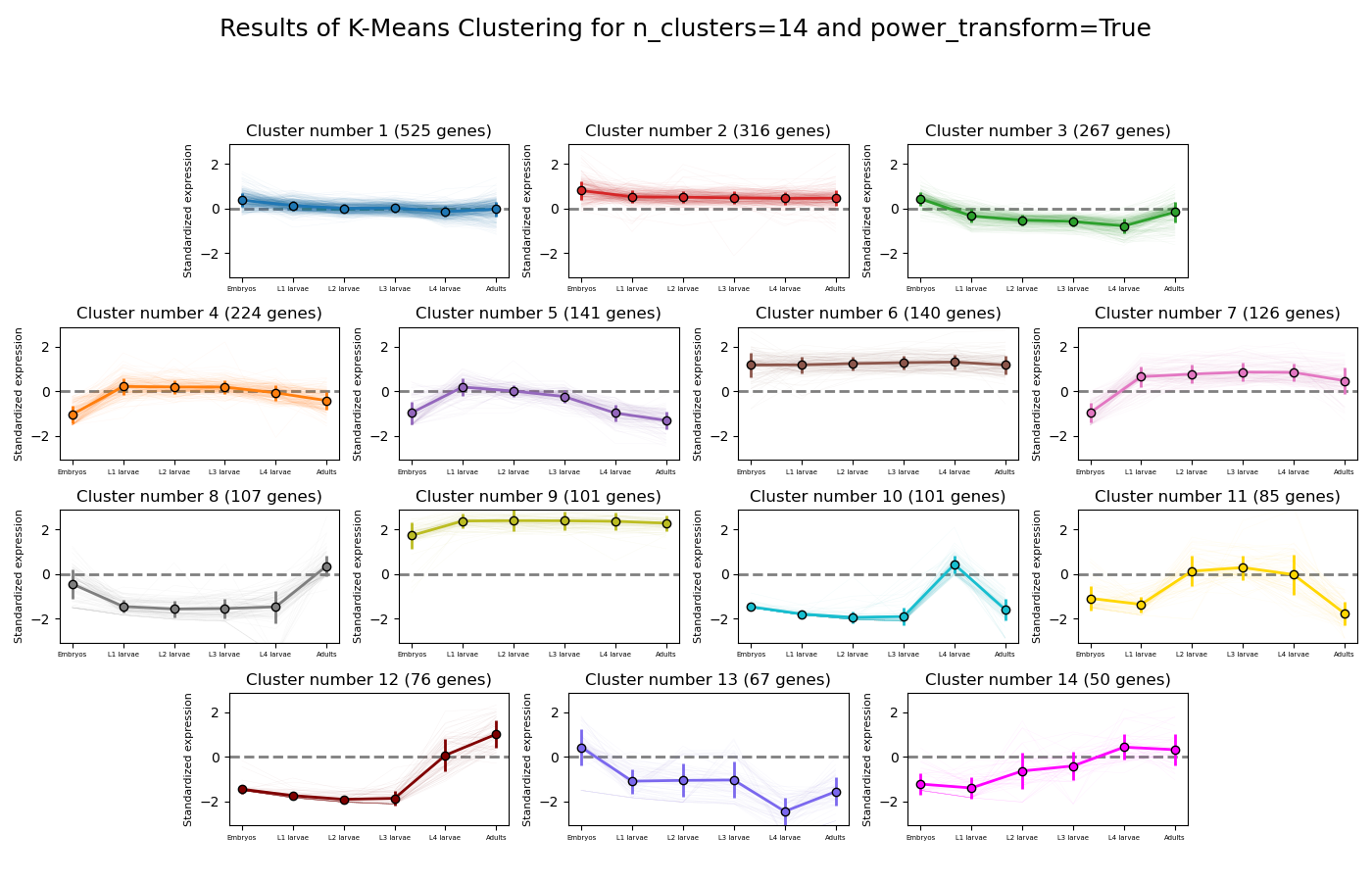
Example plot of split_kmeans(plot_style=’all’)
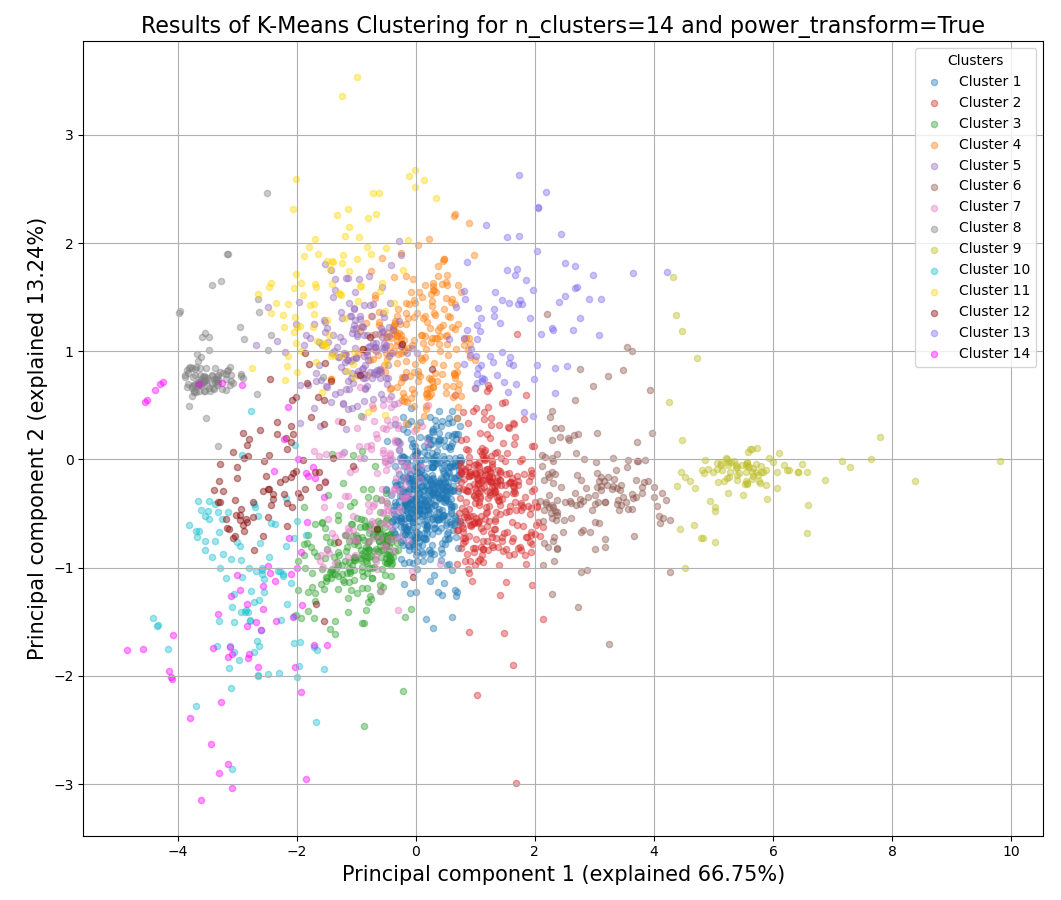
Example plot of split_kmeans()